- Protein family review
- Published:
The lamin protein family
Genome Biology volume 12, Article number: 222 (2011)
Summary
The lamins are the major architectural proteins of the animal cell nucleus. Lamins line the inside of the nuclear membrane, where they provide a platform for the binding of proteins and chromatin and confer mechanical stability. They have been implicated in a wide range of nuclear functions, including higher-order genome organization, chromatin regulation, transcription, DNA replication and DNA repair. The lamins are members of the intermediate filament (IF) family of proteins, which constitute a major component of the cytoskeleton. Lamins are the only nuclear IFs and are the ancestral founders of the IF protein superfamily. Lamins polymerize into fibers forming a complex protein meshwork in vivo and, like all IF proteins, have a tripartite structure with two globular head and tail domains flanking a central α-helical rod domain, which supports the formation of higher-order polymers. Mutations in lamins cause a large number of diverse human diseases, collectively known as the laminopathies, underscoring their functional importance.
Gene organization and evolutionary history
The lamins were first characterized biochemically as prominent 60 to 80 kDa proteins of the nuclear lamina and eventually identified as intermediate filament (IF) proteins by sequence homology [1–6]. The name intermediate filament refers to the average diameter of assembled intermediate fibers (10 to 12 nm), which is between that of actin microfilaments (7 to 10 nm) and that of microtubules (25 nm) [7]. The nuclear lamins represent one (type V) of six subtypes of the IF superfamily, defined on the basis of genomic structure and nucleotide sequence. Lamins are present only in metazoans and seem to be restricted to the animal kingdom as no obvious homologs have been identified in the fully sequenced genomes of several lower eukaryotes, including Arabidopsis thaliana, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
Nuclear lamins are divided into A and B types on the basis of structural and protein features and expression patterns. In general, A-type lamins resemble B-type lamins over the amino-terminal head and central rod domain, but have an expanded carboxy-terminal tail domain that contains a unique 90 amino acid segment (Figure 1). B-type lamins are usually ubiquitously expressed, whereas A-type lamins are expressed in developmentally regulated temporal patterns. The differences between A- and B-type lamins in terms of protein structure, expression, localization patterns and biochemistry have been interpreted to reflect functional diversification.
Nuclear lamins: domain organization and protein structure. (a) Domain organization of the major lamins in humans. The α-helical rod domain comprises four segments, 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B (yellow), which are separated by linker segments, L1, L12 and L2. The tail domain contains a nuclear localization signal, an immunoglobulin domain (green), and a conserved CAAX box, which undergoes farnesylation. (b) The structure of a portion of the α-helical rod domain corresponding to human lamin A segment 2B (PDB code: 1X8Y) [19]. (c) The structure of the Ig domain from human lamin A/C (PDB: 1IFR) [20].
Relative to the well-conserved cytoskeletal proteins tubulin and actin, IF proteins and lamins appeared more recently in evolutionary time and have undergone large divergence in sequence. Current evidence supports the hypothesis that all IF proteins arose from a common lamin-like progenitor, because all organisms known to have IF proteins also have lamins, but not all also have cytoplasmic IF proteins (the latter would be expected if lamins had evolved from a cytoplasmic IF). For example, the Drosophila genome encodes only two IF proteins, both of which are nuclear lamins [8], and the cnidarian Hydra vulgaris genome encodes a single IF protein, which is also a nuclear lamin [9]. In addition, the expression patterns of IF proteins indicate that lamins are the ancestral founder of the family. Expression of at least one lamin in all cell types is essential for viability, in contrast to cytoplasmic IFs, which are expressed in a cell-type- and tissue-specific pattern [10]. Sequence comparison further supports the notion of lamins as ancestral IFs. A lamin-specific 42 amino acid segment is present in primitive cytoplasmic IF proteins from some invertebrates but is absent from cytoplasmic IF proteins from all vertebrates and most invertebrates [11]. Given that the 42 amino acid segment is present in all lamins and some primitive cytoskeletal IF proteins, it seems that an ancestral lamin gave rise to the primordial cytoplasmic IF proteins, which later lost the 42 amino acid signature, probably through an exon deletion event. Furthermore, vertebrate nuclear lamins are more similar to invertebrate cytoplasmic IF proteins than they are to vertebrate cytoplasmic IF proteins, suggesting evolutionary proximity [12].
Several lines of evidence support the view that a B-type lamin appeared before A-type lamins. Almost all invertebrate lamins are B-type lamins, which are more similar to vertebrate B-type lamins than A-type lamins. Also, some invertebrates contain a single lamin, which is always a B-type lamin [9]. The intron-exon structure of the lamins supports a model in which a B-type lamin was the progenitor [13]. For example, intron positions of the human lamin B1 gene (LMNB1) are conserved in the lamin A/C (LMNA) and lamin B2 (LMNB2) genes; however, LMNB2 contains an intron between the regions encoding coil 1A and coil 1B that is not present in other IF proteins (including LMNA), indicating that LMNB2 and LMNA evolved from an LMNB1-like ancestor [13]. Moreover, in organisms with both A- and B-type lamins, such as mammals, B-type lamins are constitutively expressed in all somatic cells, whereas A-type lamins are developmentally regulated and expressed primarily in differentiated tissues.
A number of structural changes in the lamin sequences have occurred during evolution (Figure 2). Accordingly, vertebrate B-type lamins can be further classified into three major subtypes: B1, B2 and B3. The B3-type lamins are found only in amphibians and fish and are interesting because they show the general features of B-type lamins but their sequence is more similar to A-type lamins [14, 15]. The amino acid sequence variation between known B3-type lamins is markedly high, suggesting these lamins represent an ancient vertebrate lamin. The ancestor to all vertebrate lamins acquired an acidic cluster in the tail domain, which now differentiates them from invertebrate B-type lamins (Figure 2) [9]. A-type lamins have a longer carboxy-terminal tail as a result of a unique 90 amino acid insertion, which probably arose through an exon shuffling event [16]. Another notable structural change has occurred in tunicates, where the entire immunoglobulin (Ig) domain was deleted from the carboxy-terminal tail [17].
Phylogenetic relationships of metazoan lamins. An unrooted phylogenetic tree using an alignment of 31 lamin coding sequences [127]. Evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method and evolutionary distances were computed using the maximum composite likelihood method [128, 129]. The tree is drawn to scale with branch lengths proportional to the evolution distances. In general, all invertebrate lamins are B-type lamins. The exception is Drosophila LamC, which is considered an A-type lamin [130]. Vertebrate B-type lamins subdivide into three separate clades, B1, B2 and B3, the latter being specific to amphibians and fish. A-type lamins evolved from a Lamin B1-like ancestor and are unique to vertebrates. Major structural changes of lamins during evolution are indicated: the minus sign indicates a 90 amino acid deletion in the conserved Ig domain from tunicates (urochordate subphylum) [9]; the asterisk indicates the addition of 6 to 12 negatively charged amino acids within the tail domain of all lamins in the vertebrate lineage [9]; and the plus sign indicates the acquisition of an extra exon (exon 11), encoding 90 amino acids, in the tail domain of vertebrate A-type lamins [13].
Lamins are alternatively spliced to create multiple isoforms. The genomes of mammals encode three lamin genes, LMNA, LMNB1 and LMNB2, which collectively express at least seven protein isoforms. LMNA is alternatively spliced producing at least four isoforms: the two major isoforms lamin A and C, and the two minor isoforms C2 and AΔ10. Lamin A and C are identical for the first 566 amino acids, but lamin C lacks 98 amino acids at the carboxyl terminus that are present in pre-lamin A (before post translational processing) and contains a unique six amino acid carboxyl terminus (Figure 1). One major difference between lamins A and C is the absence in lamin C of the CAAX box, which is modified by farnesylation and has a role in targeting the lamins to the inner nuclear membrane. Some lamin isoforms are highly tissue-specific, such as human lamin B3, an alternatively spliced isoform of LMNB2, which is restricted to the male germ line [18]. Other lamin isoforms, such as lamins A and C, are ubiquitously expressed in virtually all differentiated cells. The functional significance of individual lamin isoforms is largely unknown. Overall, vertebrates encode more lamin genes and produce isoforms to a greater extent than invertebrates. Differential expression of different lamin isoforms creates functionally and structurally unique nuclear laminas. Whatever the roles of each lamin isoform, it is generally thought that increases in the numbers of lamin isoforms, either by gene duplications and/or alternative splicing, may have helped to meet the functional demands of increasing cellular variety and complexity.
Characteristic structural features
Like all IF proteins, nuclear lamins have a tripartite structure consisting of a long α-helical domain flanked by globular amino-terminal (head) and carboxy-terminal (tail) domains (Figure 1). The central α-helical or rod domain spans approximately half of the lamin molecule (about 350 residues) and comprises four α-helical segments termed 1A, 1B, 2A and 2B. Each α-helical segment has heptad-repeat periodicity, characteristic of coiled-coil proteins, and is connected by short intervening sub-domains denoted L1, L12 and L2. The 2.2 Å structure of part of the carboxy-terminal coiled-coil segment 2B from human lamin A has been solved (Figure 1b), opening the way for more detailed studies on lamin assembly [19]. The amino-terminal head domain of the lamins is variable in size but is generally shorter than the same domain found in cytoplasmic IF proteins (which are about 40 to 100 residues long). The carboxy-terminal tail domain contains a nuclear localization signal, an Ig domain and a CAAX box (Figure 1). The structure of the human lamin A/C Ig domain contains a characteristic Ig fold and forms a compact β sandwich comprising two β sheets formed from nine β strands connected by short loops [20, 21]. The Ig domain is common to many proteins and mediates diverse protein-protein and protein-ligand interactions, which involve virtually every surface of the Ig domain. The Ig domains in lamins are suggested to represent a new class on the basis of the connectivity of strands and the presence of ancillary β strands, which may confer unique protein interaction properties [20].
Dimerization, polymerization and higher-order assembly of the nuclear lamins
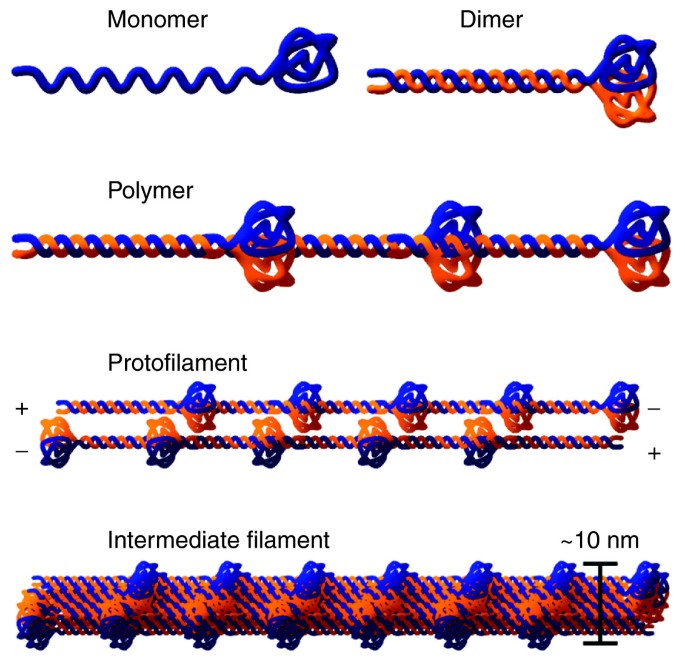
Lamins form extensive higher-order polymers (Figure 3). The ultrastructure of the nuclear lamina is best characterized in amphibian oocytes and consists of IF-like lamin filaments about 10 nm in diameter arranged in a regular woven meshwork pattern [22, 23]. This pattern contrasts somewhat with mammalian cells, where only irregular filamentous meshworks have been observed [24, 25].
Schematic model of lamin polymers. Lamin dimers form from monomers that associate in a parallel, head-to-head manner, forming a coiled coil though the central α-helical domain. Lamin polymers then assemble by association of dimers in a polar head-to-tail manner through a staggered 2 to 4 nm overlap of the highly conserved amino- and carboxy-terminal rod domain ends. Protofilaments are finally produced through anti-parallel association of two lamin polymers. Between three and four protofilaments associate laterally to form an intermediate filament about 10 nm in diameter.
Lamins dimerize using their α-helical rod domain, which contains the characteristic coiled-coil heptad repeat pattern. Coiled-coiled heptad repeats a and d preferentially contain hydrophobic residues and repeats e and g charged residues. Along the axis of the α helix is a hydrophobic seam, which acts as a dimerization interface between two lamin proteins, oriented in a parallel, unstaggered manner. Each α helix coils around the other, resulting in the lamin dimer, the basic building block of higher-order lamin assemblies (Figure 3). Electron microscopy studies show that the lamin dimer forms a rod about 50 nm long flanked at one end by two tightly packed globules, which correspond to two globular carboxy-terminal tail domains [26]. Interactions between A- and B-type lamins are possible. Pre-lamin A, lamin A, lamin B1 and lamin C can form homo- and hetero-dimers when ectopically expressed in yeast and in in vitro binding assays [27, 28]. The precise abundance of each species in vivo is not known, but the cellular ratio of the lamins is non-stoichiometric [29].
Higher-order polymerization of lamins involves head-to-tail parallel association between two or more lamin dimers, resulting in a lamin polymer (Figure 3). Head-to-tail association of lamin dimers involves an overlap of the highly conserved amino-terminal part of coil 1A and a carboxy-terminal part of coil 2B [19]. This head-to-tail association is unique to lamins, contrasting with the overlapping, half-staggered, anti-parallel side-by-side association of dimers observed for cytoplasmic IF proteins. The relatively short amino-terminal head domain is important for the formation of head-to-tail polymers in vitro and for IF formation in vivo [30]. The head domain requirement can be traced to 20 highly conserved residues, which include phosphorylation sites for cell-cycle dependent kinase 2 (CDC2), which is known to have a role in lamin disassembly in mitosis [31].
The study of higher-order lamin structures has been hampered by the difficulty of producing 10-nm filaments in vitro. So far, the Caenorhabditis elegans lamin is the only lamin that has been successfully assembled into 10 nm IF-like filaments in vitro [26, 32]. This B-type lamin has a truncated carboxy-terminal tail domain, possibly explaining the different assembly properties. It is also possible that formation of 10 nm filaments depends on the presence of membranes that are absent from the in vitro systems. Instead, most lamins form paracrystalline arrays in vitro, which display a unique axial repeat pattern [33].
Heterotypic lamin dimers can interact to form mixed isoform polymers in vitro [34]. However, it is unclear whether in vivo individual filaments contain both types of lamins within the same filament or whether lamins segregate into distinct filaments. Following mitosis, lamin A incorporates into the membrane after lamin B, suggesting that nuclear IFs are homotypic [35]. Nevertheless, this does not exclude the possibility of eventual reorganization of the nascent lamina or integration of heterotypic interactions, as suggested by high-resolution images of a mammalian somatic lamina that demonstrate domains of segregation and domains of overlap juxtaposed within the same nucleus [24].
Post-translational modifications
Lamins are post-translationally modified in several ways. Almost all lamins contain a CAAX box at the carboxyl terminus, which serves as a substrate for post-translational farnesylation. This is achieved in three successive steps starting with the isoprenylation of the cysteine, followed by the proteolytic cleavage of the AAX motif and finally the carboxy-methylation of the farnesylated cysteine. The hydrophobic farnesyl moiety is thought to facilitate localization to and retention at the nuclear envelope. Nevertheless, carboxy-terminal farnesylation is not absolutely required for lamina localization because lamin C does not contain a CAAX box but does localize to the nuclear envelope. Once localized to the nuclear envelope, lamin A is processed further by the proteolytic removal of the carboxy-terminal 18 amino acids, including the farnesyl group, whereas B-type lamins retain the farnesyl moiety in their mature form [33].
Lamins are phosphorylated by multiple kinases and contain many conserved phosphorylation sites, with more than 30 known sites in human A-type lamins alone [36]. Three kinases known to modify and modulate lamins' activities are CDC2, protein kinase C (PKC) and protein kinase A (PKA). The mitotic kinase CDC2 induces lamin disassembly by phosphorylating conserved residues within the head and coiled-coil 2B domains [31]. Phosphorylation of Thr19, Ser22 and Ser392 causes depolymerization of lamin filaments in mitosis and meiosis. PKA phosphorylation sites are highly conserved and when phosphorylated inhibit lamin polymerization [37]. In addition, phosphorylation by PKC is known to regulate lamin uptake into the nucleus [38].
Lamin A also has two sumoylation consensus sites, one within the rod domain and another within the tail domain. Substitutions (E203G and E203K) within the rod domain disrupt the canonical SUMO E2 site, resulting in lower levels of sumoylated lamin in vivo and altered subnuclear localization [39].
Localization and function
Expression
B-type lamins are constitutively expressed in most cell types, whereas A-type lamins are developmentally regulated, being predominantly expressed in most differentiated cell types [40]. However, certain cells of the hematopoietic system do not express A-type lamins even when fully differentiated [41]. In mammalian germ cells and pronuclei, expression is limited to the two atypical lamin isoforms lamin B3 and C2, respectively, which are detected only in germ cells but are otherwise not expressed [18, 42]. In fish, amphibians and birds the species-specific lamin B3 (LIII) is expressed in oocytes. A- and B-type lamins are also found in fertilized mammalian eggs until 2 to 4 cleavage divisions, when A-type lamins are no longer detected. As embryogenesis proceeds, A-type lamins are again detected on day 8 to 9 in extra-embryonic tissues and on day 12 in the embryo itself [41, 43]. Mouse and human embryonic stem cells express lamins B1 and B2 but not lamins A or C. When embryonic stem cells move towards differentiation, lamin A/C is detected immediately before the pluripotent Oct-3/4 gene is downregulated, and immediately after stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 (SSEA-4) is activated. Interspecies differences in lamin expression have also been noted: lamin A is highly expressed in circulating erythrocytes in Gallus gallus (chicken) but is absent from the same cell type in amphibians [44, 45]. Because A-type lamins usually appear after cellular differentiation initiates, it is thought that A-type lamins facilitate 'locking-in' of the differentiated state [41].
Localization
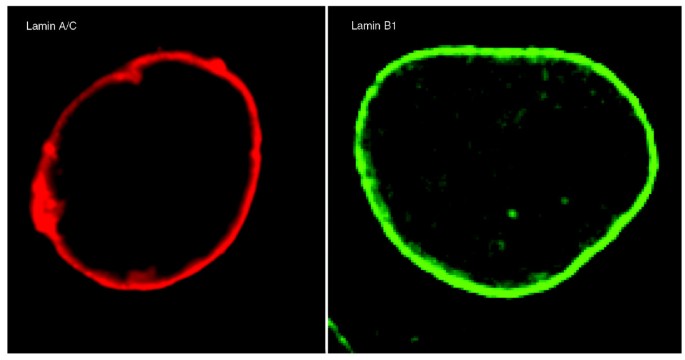
As expected from their incorporation into the lamina, a large portion of cellular lamin is found in an insoluble pool at the nuclear rim (Figure 4). There is also a pool of A-type lamins within the nucleoplasm, which is distinct from peripheral lamin A, in that it is probably not polymerized and is more soluble [46]. The assembly state, fraction, purpose and function of the nucleoplasmic lamin A are still unknown [47, 48]. Similarly, B-type lamins are also present in the nucleoplasm. In vivo dynamics of lamins in interphase nuclei have been studied by various techniques, including fluorescence recovery after photobleaching and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy [24, 35, 49–51]. In contrast to cytoplasmic IF proteins, which seem very dynamic, nuclear lamins are relatively stable once integrated into the nuclear lamina [49]. Whereas nucleoplasmic lamin A/C is highly mobile, nucleoplasmic lamins B1 and B2 are relatively immobile, indicating that A- and B-type lamins have separate organizational states [24]. Cell-cycle-related changes to lamin protein dynamics have also been reported. For instance, lamina-associated lamin B1 associates with the lamina with a half-life of about 10 minutes during the initial stages of G1, which increases to about 2 hours in a later part of G1 [35].
Lamins have pivotal roles in nuclear reassembly after cell division. During mitosis, when the nuclear envelope breaks down and the lamina disassembles, A-type lamins are solubilized and distributed throughout the cytoplasm, whereas B-type lamins maintain close associations with the nuclear membrane. The differences in membrane attachment during mitosis are attributed to whether the lamin protein is farnesylated. Mature lamin B retains its farnesylation moiety, which anchors B-type lamins to the membrane during mitosis, whereas the farnesylation moiety is removed from lamin A, rendering it more soluble [52]. To facilitate disassembly of the lamina, lamins are phosphorylated by PKC and are dephosphorylated by type 1 protein phosphatase during reassembly [53]. When a nascent nuclear envelope forms around condensed chromosomes, A-type lamins are imported into the nucleus along with additional B-type lamins [35, 54].
Lamins are early targets for caspase degradation in cells undergoing apoptosis [55, 56]. Caspase-6 and caspase-3 are the major proteases responsible for A- and B-type lamin degradation [57]. At the onset of apoptosis, before detectable DNA cleavage or chromatin condensation occurs, lamins are cleaved at caspase recognition sites located within the L12 linker region and expression of uncleavable mutant lamin protein delays the onset of apoptosis [58]. Time-lapse experiments of green-fluorescent-protein-tagged lamins suggest that A- and B-type lamins have different dynamics following their initial cleavage [59]. A-type lamins are thought to rapidly translocate to the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, whereas B-type lamins remain at the nuclear periphery.
Mechanisms
Mechanical properties of the nucleus
From their primary sequence and their grouping within the IF superfamily, the lamins were originally hypothesized to provide mechanical support for the nucleus, conceivably as tensegrity elements that specify nuclear morphology and resistance to deformation [22]. In support of this, studies using Xenopus nuclear assembly systems show that cell-free extracts depleted of lamins assemble small and fragile nuclei [60]. Conversely, ectopic expression of the germ-cell-specific lamin B3 isoform, which lacks the amino terminus and part of the α-helical domain, in somatic cells induces a hook-shaped nuclear morphology reminiscent of spermatocytes [61]. Additional studies have demonstrated that human cells expressing a variety of lamin mutations often show a range of nuclear morphological phenotypes [62]. Fibroblast nuclei from Lmna-/- mice are deformed more easily and to a greater extent than those from Lmna+/+ littermates [63]. These nuclei are also more fragile, less resistant to physical compression, and deform in an isotropic manner, in contrast to the anisotropic deformation observed in Lmna+/+ nuclei [64]. Furthermore, the absence of lamin A/C from embryonic stem cells has been suggested as an explanation for the more malleable and deformable nuclei of this cell type [65]. The extent of B-type lamin involvement in nuclear mechanics is not as well understood because loss of lamin B1 from murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) causes nuclear blebbing, but does not seem to affect mechanical properties [66].
Protein interactions
In addition to A- and B-type lamin interactions, numerous functionally diverse proteins are known to interact with the nuclear lamins, including retinoblastoma 1, c-Fos, thymopoietin (LAP2) and emerin (Figure 5). Lamins are part of a nuclear framework supporting multi-protein complexes involved in several nuclear functions. The majority of lamin-interacting proteins identified so far come from studies focused on A-type lamins. More than 30 direct and more than 100 indirect interactions have been identified using various proteomics-based studies [67, 68]. The extensive list of interaction partners further supports the notion of the lamina functioning as an intranuclear platform. The nature and function of each interaction probably varies, possibly in a tissue-specific manner. Analyses of the nuclear envelope from multiple tissues show the protein complement is highly variable between tissues, supporting a model of tissue-specific lamin A/C roles [69].
Functions of the nuclear lamina. A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions. (a) The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through association with chromatin-modifying and regulatory proteins. (b) The lamina regulates gene expression by sequestering transcription factors at the nuclear envelope, which limits their availability in the nucleoplasm. (c) It also mediates structural linkages between the nucleus and cytoskeleton, through the LINC complex consisting of lamins, an inner nuclear membrane protein, and an interacting outer nuclear membrane protein, which in turn binds cytoskeletal elements. (d) The lamina also provides a platform for assembly of protein complexes involved in signal transduction pathways. P, phosphate.
Cytoskeletal connections
Nuclei are mechanically linked to the cytoskeleton through lamin-interacting proteins that span the nuclear envelope (Figure 5). This linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex consists of lamin-interacting proteins SUN1 or SUN2, which span the inner nuclear membrane where they, in turn, interact with a member of the nesprin family of proteins in the luminal space [70]. Nesprins span the outer nuclear membrane, where they associate in the cytoplasm with various cytoskeletal elements. The LINC complex has been implicated in serving functions important for nuclear migration, positioning, morphology and mechanics [71, 72].
Lamins and chromatin
Lamins are global regulators of chromatin (Figure 5). Transcriptionally silent regions of the genome, such as centromeres, telomeres and the inactive X chromosome, are preferentially positioned at the nuclear lamina [73, 74]. A direct role for lamins in the regulation of chromatin was demonstrated in studies of cardiomyocytes and MEFs derived from Lmna-/- mice, which show a partial loss of peripheral heterochromatin, ectopic chromosome condensation and mis-positioning of centromeric heterochromatin [75–77]. Disengagement and/or loss of heterochromatin are also observed in cells expressing a variety of mutant lamin A proteins [78–80]. Global heterochromatic changes induced by lamin perturbation are often mirrored by altered levels of chromatin-associated epigenetic histone marks; for example, decreased levels of the heterochromatin markers histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) and H3K27me3 and increased levels of H4K20me3. Ectopic lamin expression also influences chromatin organization and associated histone marks; for example, hypermethylated H3K4, a mark of active genes, decreases following overexpression of wild-type lamin A in C2C12 myoblasts [81].
Lamins have at least two chromatin-binding regions. One chromatin interaction domain is located in the tail region between the end of the rod domain and the Ig domain, and the other is within the rod domain [82, 83]. Chromatin interactions are probably mediated through histones and/or chromatin-associated proteins, but lamins bind nonspecifically to DNA in vitro through contacts in the minor groove of the double helix [82, 84]; however, lamins associate with sequences known as scaffold/matrix attachment regions, which are involved in transcriptional regulation, DNA replication, chromosome condensation and chromatin organization [85]. Genome-wide mapping techniques have identified genome regions that preferentially associate with lamins, known as lamin-A-associated domains (LADs) [86]. These domains are generally gene-poor and are proposed to represent a repressive chromatin environment.
DNA damage and repair
Recent studies have hinted at a role for lamins in DNA repair. Most of these studies have focused on the effects of expressing an unprocessed lamin A protein, which causes the premature aging disorder Hutchinson Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS). The mutant lamin A protein, named progerin, expressed in HGPS patients has a deletion in the tail domain and consequently remains permanently farnesylated. Cells expressing progerin have a delayed recruitment of the repair factor p53-binding protein (53BP1) to sites of DNA damage, show increased levels of the double-stranded break marker γ-H2AX, and are more sensitive to DNA damaging agents [87]. Progerin expression also affects the localization and expression of the key DNA damage regulators ATR and ATM and the double-stranded break repair factors Rad50 and Rad51 [88]. Taken together, these studies suggest the necessity of normal lamin A function in repair of DNA damage. However, the mechanistic details linking lamins and DNA damage have yet to be fully elucidated.
Cellular signaling
Many studies have documented a link between lamins and signal transduction pathways important for cellular differentiation and homeostasis (Figure 5) [89]. Through protein-protein interactions, lamins are thought to regulate the activity and availability of proteins within signaling cascades, including the retinoblastoma (Rb)/E2F, Wnt/β-catenin, transforming growth factor (TGF)β/Mothers against Decapentaplegic (SMAD) and mitogen activating protein (MAP) kinase pathways. A well characterized example is AP1 (Jun/Fos) regulation through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/MAP kinase signaling. In this case, mitogen stimulation leads to the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, causing it to translocate into the nucleus. Once there, phosphorylated ERK1/2 binds to lamin A and phosphorylates c-Fos, which is normally sequestered at the nuclear envelope through interaction with lamin A. The phosphorylation of c-Fos causes its release from the nuclear envelope, allowing dimerization with c-Jun and activation of AP1 immediate-early genes [90]. Another example is the regulation of SMAD proteins, which mediate signaling downstream of TGFβ [91]. Following induction, SMADs are phosphorylated by TGFβ-receptor kinases, which stimulate their binding with co-SMADs, accumulation in the nucleus, and assembly with gene-specific transcription factors. A-type lamins modulate SMAD activity by binding to SMADs and promoting inactivation through their sequestration at the nuclear envelope. A-type lamins can also bind the SMAD antagonists MAN1 and PP2A, which dampen SMAD activity through sequestration and dephosphorylation [92].
Transcription
Several lines of evidence support the view that lamins mediate transcriptional regulation. Developmentally associated changes in lamin expression often coincide with increased RNA polymerase II activity and accumulation of cell-type-specific transcripts [93]. Disruption of lamin organization, by expressing dominant-negative A-type lamins, inhibits RNA polymerase II transcription and perturbs the localization of the initiation factor TATA-binding protein [94, 95]. Lamin A/C associates with numerous transcriptional regulators, either directly or indirectly, including Rb, Gcl, Mok2, cFos and Srebp1 [96]. The transcription factor Oct-1 is sequestered at the nuclear envelope through associations with lamin B1, which is important for its regulation of oxidative stress gene expression [97]. Thus, lamins bind many transcriptional regulators and can affect gene expression by sequestration of these factors or by influencing the assembly of core transcriptional complexes [90, 97].
DNA replication
Lamins have also been implicated in replication. In assembly systems, lamin-depleted Xenopus nuclear extracts produce nuclei that are no longer competent to replicate their DNA [60, 98]. Additional support comes from an observed colocalization of lamins with sites of bromodeoxyuridine incorporation and at replication foci with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) [99–101]. Expression of dominant-negative lamin B mutants, lacking the central rod domain, has been reported to inhibit DNA replication [102–104].
Human diseases: the laminopathies
Lamins have more recently garnered a surge of interest because of discoveries that lamin mutations, primarily in LMNA, are associated with numerous heritable human diseases [105–108]. These 'laminopathies' currently comprise 17 distinct diseases and include forms of cardiomyopathy, muscular dystrophy, lipodystrophy and aging-related progeria (Figure 6). Laminopathies manifest predominantly in mesenchymal tissues, such as skeletal muscle, heart, adipose tissue, connective tissue and bone, and fall into two general groups: those that affect specific tissues in an isolated manner and those involving multiple tissue systems. There is significant phenotypic overlap in laminopathies, leading to the suggestion that laminopathies are a 'functional continuum' of related diseases rather than separable disorders [109].
Summary of disease-associated LMNA mutations mapped onto the human lamin A protein [110]. Colors indicate the class of disease. Red, laminopathies with preferential involvement of skeletal and cardiac muscle, which range from muscle-wasting muscular dystrophies to cardiac conduction defects; blue, lipodystrophies, which specifically affect adipose tissues; brown, neuropathy disorders, which affect the motor and sensory neurons of the peripheral nervous system; green, 'systemic' laminopathies, which are heterogeneous disorders involving multiple tissue systems; purple, mutations associated with premature aging disorders. Mutations affecting amino acids 1 to 566 affect both lamin A and C isoforms, whereas mutations found in the carboxy-terminal 566 to 664 amino acids are specific to the lamin A isoform. fs, frameshift; del, deletion; ins, insertion; c, coding.
About 90% of known disease-associated polymorphisms are missense mutations, which are distributed throughout the lamin A/C protein [110]. A clear genotype-phenotype relationship has not emerged despite the description of over 1,000 sequence polymorphisms and about 350 disease-associated mutations (Figure 6). The creation of mouse models based on laminopathy mutations has provided some clues [111]. Efforts to unravel and explain the pathophysiological mechanisms are possibly confounded by largely unexplored genetic modifiers [112–114].
In contrast to numerous LMNA-related diseases, only two diseases are reported to be associated with mutations in the LMNB1 and LMNB2 genes. A duplication of LMNB1 resulting in higher LMNB1 dosage/expression in brain tissues is associated with the neurological condition autosomal-dominant leukodystrophy [107]. Several rare LMNB2 missense mutations are purportedly associated with acquired partial lipodystrophy [106]. The finding that expression of at least one B-type lamin in mammalian cells is essential for viability, and their ubiquitous expression, might explain the relative paucity of LMNB-associated diseases [10]. This seems to be the case because homozygous mice carrying insertional mutations in LMNB1 die at birth with lung and bone defects. Mice deficient for lamin B2 also die postnatally and display a lissencephaly phenotype, due in part to disrupted nuclear movement that is linked to defective neuronal migration [115].
The pathological mechanisms of these diseases remain obscure, although several models have been proposed. In a structural model, expression of lamin A/C variants causes nuclear fragility and increased sensitivity to physical stressors [116]. Other models have focused on the cellular roles of lamins, suggesting that LMNA mutations alter normal gene expression profiles, either directly through chromatin interactions or indirectly by disrupting protein-protein interactions [116]. One challenge has been to adequately explain how ubiquitously expressed proteins give rise to tissue-restricted diseases. The tissue-specific lamin A/C model predicts the existence of tissue-specific lamin A/C partners whose interaction is disrupted by particular lamin A protein variants.
Lamins are misregulated in some cancers, possibly making them useful as biomarkers. A-type lamin expression is decreased by about 80% in small-cell lung cancer lines but is high and unchanged in non-small-cell lung cancer lines [117]. Similarly, in primary lung carcinomas, primarily A-type but also to some extent B-type lamins show reduced expression [118], and both A- and B-type lamins are undetectable or reduced in most primary colon carcinomas, adenomas and primary gastric cancers [119]. However, reduced lamin expression does not always correlate with cancer tissues. Lamin A/C showed higher expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas than in normal skin [120, 121]. Paradoxically, the absence of lamin A in basal cell carcinomas is correlated with rapid tumor proliferation rates, whereas the absence of lamin C is correlated with a slower proliferation rate. Lamin A is reported to be a promising biomarker for grading prostate cancers and may aid in prognosis [122]. In addition, increased levels of A-type lamins in colorectal cancer tissues correlates with a twofold increase in cancer-related mortality [123]. Lamin B1 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tumors and correlates with tumor size, stage and nodule number [124]. Furthermore, elevated levels of plasma lamin B1 can predict early stage hepatocellular carcinoma and might also prove to be a useful clinical biomarker for colorectal cancers [124, 125].
Frontiers
As architectural proteins of the nucleus, the lamins are positioned at the intersection of numerous diverse nuclear processes. Lamins are among the most prominent and best studied proteins in animals, yet many of their properties remain unknown. The lamin protein family is especially intriguing in light of its association with a large number of human diseases. Unraveling the basic functions of lamins will be essential to shed light on the molecular mechanisms of these diseases.
The meshwork of 10 nm filaments is the functional entity of lamins that must be understood if we are to understand different lamin properties and the consequences of lamin mutations. Already, some disease-associated lamin mutations are known to affect lamina formation [126]. Defective lamin assemblies may ultimately have an impact on the mechanical properties of the nucleus and/or interfere with nuclear processes, including signaling, nuclear import, transcription, DNA replication and DNA repair. A better understanding of the composition of the lamina and the influence of different lamin isoforms on its formation and function will provide additional important clues. Perhaps the most important goal will be to understand the tissue-specificity of lamins. Why do some LMNA mutations affect a particular tissue or subset of tissues despite near-ubiquitous expression of lamin A in all tissues? And why do different LMNA mutations manifest as dramatically different diseases?
References
Aaronson RP, Blobel G: Isolation of nuclear pore complexes in association with a lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975, 72: 1007-1011. 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1007.
Gerace L, Blum A, Blobel G: Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978, 79: 546-566. 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546.
McKeon FD, Kirschner MW, Caput D: Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986, 319: 463-468. 10.1038/319463a0.
Lin F, Worman HJ: Structural organization of the human gene (LMNB1) encoding nuclear lamin B1. Genomics. 1995, 27: 230-236. 10.1006/geno.1995.1036.
Lin F, Worman HJ: Structural organization of the human gene encoding nuclear lamin A and nuclear lamin C. J Biol Chem. 1993, 268: 16321-16326.
Fisher DZ, Chaudhary N, Blobel G: cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986, 83: 6450-6454. 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450.
Ishikawa H, Bischoff R, Holtzer H: Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968, 38: 538-555. 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538.
Riemer D, Weber K: The organization of the gene for Drosophila lamin C: limited homology with vertebrate lamin genes and lack of homology versus the Drosophila lamin Dmo gene. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994, 63: 299-306.
Erber A, Riemer D, Hofemeister H, Bovenschulte M, Stick R, Panopoulou G, Lehrach H, Weber K: Characterization of the Hydra lamin and its gene: a molecular phylogeny of metazoan lamins. J Mol Evol. 1999, 49: 260-271. 10.1007/PL00006548.
Harborth J, Elbashir SM, Bechert K, Tuschl T, Weber K: Identification of essential genes in cultured mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. J Cell Sci. 2001, 114: 4557-4565.
Riemer D, Weber K: Common and variant properties of intermediate filament proteins from lower chordates and vertebrates; two proteins from the tunicate Styela and the identification of a type III homologue. J Cell Sci. 1998, 111: 2967-2975.
Weber K, Plessmann U, Ulrich W: Cytoplasmic intermediate filament proteins of invertebrates are closer to nuclear lamins than are vertebrate intermediate filament proteins; sequence characterization of two muscle proteins of a nematode. EMBO J. 1989, 8: 3221-3227.
Stick R: The gene structure of Xenopus nuclear lamin A: a model for the evolution of A-type from B-type lamins by exon shuffling. Chromosoma. 1992, 101: 566-574. 10.1007/BF00660316.
Yamaguchi A, Yamashita M, Yoshikuni M, Nagahama Y: Identification and molecular cloning of germinal vesicle lamin B3 in goldfish (Carassius auratus) oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 2001, 268: 932-939. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2001.01952.x.
Hofemeister H, Kuhn C, Franke WW, Weber K, Stick R: Conservation of the gene structure and membrane-targeting signals of germ cell-specific lamin LIII in amphibians and fish. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002, 81: 51-60. 10.1078/0171-9335-00229.
Riemer D, Dodemont H, Weber K: Analysis of the cDNA and gene encoding a cytoplasmic intermediate filament (IF) protein from the cephalochordate Branchiostoma lanceolatum; implications for the evolution of the IF protein family. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992, 58: 128-135.
Riemer D, Wang J, Zimek A, Swalla BJ, Weber K: Tunicates have unusual nuclear lamins with a large deletion in the carboxyterminal tail domain. Gene. 2000, 255: 317-325. 10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00323-1.
Furukawa K, Hotta Y: cDNA cloning of a germ cell specific lamin B3 from mouse spermatocytes and analysis of its function by ectopic expression in somatic cells. EMBO J. 1993, 12: 97-106.
Strelkov SV, Schumacher J, Burkhard P, Aebi U, Herrmann H: Crystal structure of the human lamin A coil 2B dimer: implications for the head-to-tail association of nuclear lamins. J Mol Biol. 2004, 343: 1067-1080. 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.093.
Dhe-Paganon S, Werner ED, Chi YI, Shoelson SE: Structure of the globular tail of nuclear lamin. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277: 17381-17384. 10.1074/jbc.C200038200.
Krimm I, Ostlund C, Gilquin B, Couprie J, Hossenlopp P, Mornon JP, Bonne G, Courvalin JC, Worman HJ, Zinn-Justin S: The Ig-like structure of the C-terminal domain of lamin A/C, mutated in muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathy, and partial lipodystrophy. Structure. 2002, 10: 811-823. 10.1016/S0969-2126(02)00777-3.
Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L: The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986, 323: 560-564. 10.1038/323560a0.
Akey CW: Interactions and structure of the nuclear pore complex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1989, 109: 955-970. 10.1083/jcb.109.3.955.
Shimi T, Pfleghaar K, Kojima S, Pack CG, Solovei I, Goldman AE, Adam SA, Shumaker DK, Kinjo M, Cremer T, Goldman RD: The A- and B-type nuclear lamin networks: microdomains involved in chromatin organization and transcription. Genes Dev. 2008, 22: 3409-3421. 10.1101/gad.1735208.
Schermelleh L, Carlton PM, Haase S, Shao L, Winoto L, Kner P, Burke B, Cardoso MC, Agard DA, Gustafsson MG, Leonhardt H, Sedat JW: Subdiffraction multicolor imaging of the nuclear periphery with 3D structured illumination microscopy. Science. 2008, 320: 1332-1336. 10.1126/science.1156947.
Karabinos A, Schunemann J, Meyer M, Aebi U, Weber K: The single nuclear lamin of Caenorhabditis elegans forms in vitro stable intermediate filaments and paracrystals with a reduced axial periodicity. J Mol Biol. 2003, 325: 241-247. 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01240-8.
Ye Q, Worman HJ: Protein-protein interactions between human nuclear lamins expressed in yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1995, 219: 292-298. 10.1006/excr.1995.1230.
Georgatos SD, Stournaras C, Blobel G: Heterotypic and homotypic associations between the nuclear lamins: site-specificity and control by phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988, 85: 4325-4329. 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4325.
Worman HJ, Lazaridis I, Georgatos SD: Nuclear lamina heterogeneity in mammalian cells. Differential expression of the major lamins and variations in lamin B phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988, 263: 12135-12141.
Isobe K, Gohara R, Ueda T, Takasaki Y, Ando S: The last twenty residues in the head domain of mouse lamin A contain important structural elements for formation of head-to-tail polymers in vitro. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007, 71: 1252-1259. 10.1271/bbb.60674.
Peter M, Nakagawa J, Doree M, Labbe JC, Nigg EA: In vitro disassembly of the nuclear lamina and M phase-specific phosphorylation of lamins by cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990, 61: 591-602. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90471-P.
Ben-Harush K, Wiesel N, Frenkiel-Krispin D, Moeller D, Soreq E, Aebi U, Herrmann H, Gruenbaum Y, Medalia O: The supramolecular organization of the C. elegans nuclear lamin filament. J Mol Biol. 2009, 386: 1392-1402. 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.024.
Goldberg MW, Huttenlauch I, Hutchison CJ, Stick R: Filaments made from A- and B-type lamins differ in structure and organization. J Cell Sci. 2008, 121: 215-225. 10.1242/jcs.022020.
Kapinos LE, Schumacher J, Mucke N, Machaidze G, Burkhard P, Aebi U, Strelkov SV, Herrmann H: Characterization of the head-to-tail overlap complexes formed by human lamin A, B1 and B2 "half-minilamin" dimers. J Mol Biol. 2010, 396: 719-731. 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.001.
Moir RD, Yoon M, Khuon S, Goldman RD: Nuclear lamins A and B1: different pathways of assembly during nuclear envelope formation in living cells. J Cell Biol. 2000, 151: 1155-1168. 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1155.
Eggert M, Radomski N, Tripier D, Traub P, Jost E: Identification of phosphorylation sites on murine nuclear lamin C by RP-HPLC and microsequencing. FEBS Lett. 1991, 292: 205-209. 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80868-4.
Molloy S, Little M: p34cdc2 kinase-mediated release of lamins from nuclear ghosts is inhibited by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Exp Cell Res. 1992, 201: 494-499. 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90299-N.
Collas P, Thompson L, Fields AP, Poccia DL, Courvalin JC: Protein kinase C-mediated interphase lamin B phosphorylation and solubilization. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272: 21274-21280. 10.1074/jbc.272.34.21274.
Zhang YQ, Sarge KD: Sumoylation regulates lamin A function and is lost in lamin A mutants associated with familial cardiomyopathies. J Cell Biol. 2008, 182: 35-39. 10.1083/jcb.200712124.
Schatten G, Maul GG, Schatten H, Chaly N, Simerly C, Balczon R, Brown DL: Nuclear lamins and peripheral nuclear antigens during fertilization and embryogenesis in mice and sea urchins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985, 82: 4727-4731. 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4727.
Rober RA, Weber K, Osborn M: Differential timing of nuclear lamin A/C expression in the various organs of the mouse embryo and the young animal: a developmental study. Development. 1989, 105: 365-378.
Furukawa K, Inagaki H, Hotta Y: Identification and cloning of an mRNA coding for a germ cell-specific A-type lamin in mice. Exp Cell Res. 1994, 212: 426-430. 10.1006/excr.1994.1164.
Stewart C, Burke B: Teratocarcinoma stem cells and early mouse embryos contain only a single major lamin polypeptide closely resembling lamin B. Cell. 1987, 51: 383-392.
Lehner CF, Stick R, Eppenberger HM, Nigg EA: Differential expression of nuclear lamin proteins during chicken development. J Cell Biol. 1987, 105: 577-587. 10.1083/jcb.105.1.577.
Wolin SL, Krohne G, Kirschner MW: A new lamin in Xenopus somatic tissues displays strong homology to human lamin A. EMBO J. 1987, 6: 3809-3818.
Hozak P, Sasseville AM, Raymond Y, Cook PR: Lamin proteins form an internal nucleoskeleton as well as a peripheral lamina in human cells. J Cell Sci. 1995, 108: 635-644.
Goldman AE, Moir RD, Montag-Lowy M, Stewart M, Goldman RD: Pathway of incorporation of microinjected lamin A into the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1992, 119: 725-735. 10.1083/jcb.119.4.725.
Bridger JM, Kill IR, O'Farrell M, Hutchison CJ: Internal lamin structures within G1 nuclei of human dermal fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1993, 104: 297-306.
Broers JL, Machiels BM, van Eys GJ, Kuijpers HJ, Manders EM, van Driel R, Ramaekers FC: Dynamics of the nuclear lamina as monitored by GFP-tagged A-type lamins. J Cell Sci. 1999, 112: 3463-3475.
Dahl KN, Scaffidi P, Islam MF, Yodh AG, Wilson KL, Misteli T: Distinct structural and mechanical properties of the nuclear lamina in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006, 103: 10271-10276. 10.1073/pnas.0601058103.
Daigle N, Beaudouin J, Hartnell L, Imreh G, Hallberg E, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Ellenberg J: Nuclear pore complexes form immobile networks and have a very low turnover in live mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 2001, 154: 71-84. 10.1083/jcb.200101089.
Sinensky M, Fantle K, Trujillo M, McLain T, Kupfer A, Dalton M: The processing pathway of prelamin A. J Cell Sci. 1994, 107: 61-67.
Thompson LJ, Bollen M, Fields AP: Identification of protein phosphatase 1 as a mitotic lamin phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272: 29693-29697. 10.1074/jbc.272.47.29693.
Levy DL, Heald R: Nuclear size is regulated by importin alpha and Ntf2 in Xenopus. Cell. 2010, 143: 288-298. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.012.
Oberhammer FA, Hochegger K, Froschl G, Tiefenbacher R, Pavelka M: Chromatin condensation during apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of lamin A+B, without enhanced activation of cdc2 kinase. J Cell Biol. 1994, 126: 827-837. 10.1083/jcb.126.4.827.
Lazebnik YA, Takahashi A, Moir RD, Goldman RD, Poirier GG, Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC: Studies of the lamin proteinase reveal multiple parallel biochemical pathways during apoptotic execution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995, 92: 9042-9046. 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9042.
Slee EA, Adrain C, Martin SJ: Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2001, 276: 7320-7326. 10.1074/jbc.M008363200.
Rao L, Perez D, White E: Lamin proteolysis facilitates nuclear events during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1996, 135: 1441-1455. 10.1083/jcb.135.6.1441.
Broers JL, Bronnenberg NM, Kuijpers HJ, Schutte B, Hutchison CJ, Ramaekers FC: Partial cleavage of A-type lamins concurs with their total disintegration from the nuclear lamina during apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol. 2002, 81: 677-691. 10.1078/0171-9335-00282.
Newport JW, Wilson KL, Dunphy WG: A lamin-independent pathway for nuclear envelope assembly. J Cell Biol. 1990, 111: 2247-2259. 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2247.
Furukawa K, Hotta Y: cDNA cloning of a germ cell specific lamin B3 from mouse spermatocytes and analysis of its function by ectopic expression in somatic cells. EMBO J. 1993, 12: 97-106.
Worman HJ, Bonne G: "Laminopathies": a wide spectrum of human diseases. Exp Cell Res. 2007, 313: 2121-2133. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.028.
Lammerding J, Schulze PC, Takahashi T, Kozlov S, Sullivan T, Kamm RD, Stewart CL, Lee RT: Lamin A/C deficiency causes defective nuclear mechanics and mechanotransduction. J Clin Invest. 2004, 113: 370-378.
Broers JL, Peeters EA, Kuijpers HJ, Endert J, Bouten CV, Oomens CW, Baaijens FP, Ramaekers FC: Decreased mechanical stiffness in LMNA-/- cells is caused by defective nucleo-cytoskeletal integrity: implications for the development of laminopathies. Hum Mol Genet. 2004, 13: 2567-2580. 10.1093/hmg/ddh295.
Pajerowski JD, Dahl KN, Zhong FL, Sammak PJ, Discher DE: Physical plasticity of the nucleus in stem cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104: 15619-15624. 10.1073/pnas.0702576104.
Lammerding J, Fong LG, Ji JY, Reue K, Stewart CL, Young SG, Lee RT: Lamins A and C but not lamin B1 regulate nuclear mechanics. J Biol Chem. 2006, 281: 25768-25780. 10.1074/jbc.M513511200.
Kubben N, Voncken JW, Misteli T: Mapping of protein- and chromatin-interactions at the nuclear lamina. Nucleus. 2010, 1: 460-471.
Prasad TS, Kandasamy K, Pandey A: Human Protein Reference Database and Human Proteinpedia as discovery tools for systems biology. Methods Mol Biol. 2009, 577: 67-79. 10.1007/978-1-60761-232-2_6.
Kavanagh DM, Powell WE, Malik P, Lazou V, Schirmer EC: Organelle proteome variation among different cell types: lessons from nuclear membrane proteins. Subcell Biochem. 2007, 43: 51-76. 10.1007/978-1-4020-5943-8_5.
Crisp M, Liu Q, Roux K, Rattner JB, Shanahan C, Burke B, Stahl PD, Hodzic D: Coupling of the nucleus and cytoplasm: role of the LINC complex. J Cell Biol. 2006, 172: 41-53. 10.1083/jcb.200509124.
Malone CJ, Fixsen WD, Horvitz HR, Han M: UNC-84 localizes to the nuclear envelope and is required for nuclear migration and anchoring during C. elegans development. Development. 1999, 126: 3171-3181.
Starr DA, Han M: ANChors away: an actin based mechanism of nuclear positioning. J Cell Sci. 2003, 116: 211-216. 10.1242/jcs.00248.
Fawcett DW: On the occurrence of a fibrous lamina on the inner aspect of the nuclear envelope in certain cells of vertebrates. Am J Anat. 1966, 119: 129-145. 10.1002/aja.1001190108.
Belmont AS, Zhai Y, Thilenius A: Lamin B distribution and association with peripheral chromatin revealed by optical sectioning and electron microscopy tomography. J Cell Biol. 1993, 123: 1671-1685. 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1671.
Galiova G, Bartova E, Raska I, Krejci J, Kozubek S: Chromatin changes induced by lamin A/C deficiency and the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 2008, 87: 291-303. 10.1016/j.ejcb.2008.01.013.
Nikolova V, Leimena C, McMahon AC, Tan JC, Chandar S, Jogia D, Kesteven SH, Michalicek J, Otway R, Verheyen F, Rainer S, Stewart CL, Martin D, Feneley MP, Fatkin D: Defects in nuclear structure and function promote dilated cardiomyopathy in lamin A/C-deficient mice. J Clin Invest. 2004, 113: 357-369.
Sullivan T, Escalante-Alcalde D, Bhatt H, Anver M, Bhat N, Nagashima K, Stewart CL, Burke B: Loss of A-type lamin expression compromises nuclear envelope integrity leading to muscular dystrophy. J Cell Biol. 1999, 147: 913-920. 10.1083/jcb.147.5.913.
Ognibene A, Sabatelli P, Petrini S, Squarzoni S, Riccio M, Santi S, Villanova M, Palmeri S, Merlini L, Maraldi NM: Nuclear changes in a case of X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1999, 22: 864-869. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199907)22:7<864::AID-MUS8>3.0.CO;2-G.
Scaffidi P, Misteli T: Lamin A-dependent nuclear defects in human aging. Science. 2006, 312: 1059-1063. 10.1126/science.1127168.
Scaffidi P, Misteli T: Reversal of the cellular phenotype in the premature aging disease Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Nat Med. 2005, 11: 440-445. 10.1038/nm1204.
Hakelien AM, Delbarre E, Gaustad KG, Buendia B, Collas P: Expression of the myodystrophic R453W mutation of lamin A in C2C12 myoblasts causes promoter-specific and global epigenetic defects. Exp Cell Res. 2008, 314: 1869-1880. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.02.018.
Taniura H, Glass C, Gerace L: A chromatin binding site in the tail domain of nuclear lamins that interacts with core histones. J Cell Biol. 1995, 131: 33-44. 10.1083/jcb.131.1.33.
Bruston F, Delbarre E, Ostlund C, Worman HJ, Buendia B, Duband-Goulet I: Loss of a DNA binding site within the tail of prelamin A contributes to altered heterochromatin anchorage by progerin. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584: 2999-3004. 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.05.032.
Shoeman RL, Traub P: The in vitro DNA-binding properties of purified nuclear lamin proteins and vimentin. J Biol Chem. 1990, 265: 9055-9061.
Luderus ME, den Blaauwen JL, de Smit OJ, Compton DA, van Driel R: Binding of matrix attachment regions to lamin polymers involves single-stranded regions and the minor groove. Mol Cell Biol. 1994, 14: 6297-6305.
Guelen L, Pagie L, Brasset E, Meuleman W, Faza MB, Talhout W, Eussen BH, de Klein A, Wessels L, de Laat W, van Steensel B: Domain organization of human chromosomes revealed by mapping of nuclear lamina interactions. Nature. 2008, 453: 948-951. 10.1038/nature06947.
Liu B, Wang J, Chan KM, Tjia WM, Deng W, Guan X, Huang JD, Li KM, Chau PY, Chen DJ, Pei D, Pendas AM, Cadiñanos J, López-Otín C, Tse HF, Hutchison C, Chen J, Cao Y, Cheah KS, Tryggvason K, Zhou Z: Genomic instability in laminopathy-based premature aging. Nat Med. 2005, 11: 780-785. 10.1038/nm1266.
Manju K, Muralikrishna B, Parnaik VK: Expression of disease-causing lamin A mutants impairs the formation of DNA repair foci. J Cell Sci. 2006, 119: 2704-2714. 10.1242/jcs.03009.
Andres V, Gonzalez JM: Role of A-type lamins in signaling, transcription, and chromatin organization. J Cell Biol. 2009, 187: 945-957. 10.1083/jcb.200904124.
Gonzalez JM, Navarro-Puche A, Casar B, Crespo P, Andres V: Fast regulation of AP-1 activity through interaction of lamin A/C, ERK1/2, and c-Fos at the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 2008, 183: 653-666. 10.1083/jcb.200805049.
Lin F, Morrison JM, Wu W, Worman HJ: MAN1, an integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane, binds Smad2 and Smad3 and antagonizes transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Hum Mol Genet. 2005, 14: 437-445.
Van Berlo JH, Voncken JW, Kubben N, Broers JL, Duisters R, van Leeuwen RE, Crijns HJ, Ramaekers FC, Hutchison CJ, Pinto YM: A-type lamins are essential for TGF-beta1 induced PP2A to dephosphorylate transcription factors. Hum Mol Genet. 2005, 14: 2839-2849. 10.1093/hmg/ddi316.
Benavente R, Krohne G: Change of karyoskeleton during spermatogenesis of Xenopus: expression of lamin LIV, a nuclear lamina protein specific for the male germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985, 82: 6176-6180. 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6176.
Spann TP, Goldman AE, Wang C, Huang S, Goldman RD: Alteration of nuclear lamin organization inhibits RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. J Cell Biol. 2002, 156: 603-608. 10.1083/jcb.200112047.
Kumaran RI, Muralikrishna B, Parnaik VK: Lamin A/C speckles mediate spatial organization of splicing factor compartments and RNA polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 2002, 159: 783-793. 10.1083/jcb.200204149.
Zastrow MS, Vlcek S, Wilson KL: Proteins that bind A-type lamins: integrating isolated clues. J Cell Sci. 2004, 117: 979-987. 10.1242/jcs.01102.
Malhas AN, Lee CF, Vaux DJ: Lamin B1 controls oxidative stress responses via Oct-1. J Cell Biol. 2009, 184: 45-55. 10.1083/jcb.200804155.
Meier J, Campbell KH, Ford CC, Stick R, Hutchison CJ: The role of lamin LIII in nuclear assembly and DNA replication, in cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1991, 98: 271-279.
Kennedy BK, Barbie DA, Classon M, Dyson N, Harlow E: Nuclear organization of DNA replication in primary mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 2000, 14: 2855-2868. 10.1101/gad.842600.
Johnson BR, Nitta RT, Frock RL, Mounkes L, Barbie DA, Stewart CL, Harlow E, Kennedy BK: A-type lamins regulate retinoblastoma protein function by promoting subnuclear localization and preventing proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004, 101: 9677-9682. 10.1073/pnas.0403250101.
Moir RD, Montag-Lowy M, Goldman RD: Dynamic properties of nuclear lamins: lamin B is associated with sites of DNA replication. J Cell Biol. 1994, 125: 1201-1212. 10.1083/jcb.125.6.1201.
Spann TP, Moir RD, Goldman AE, Stick R, Goldman RD: Disruption of nuclear lamin organization alters the distribution of replication factors and inhibits DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1997, 136: 1201-1212. 10.1083/jcb.136.6.1201.
Moir RD, Spann TP, Herrmann H, Goldman RD: Disruption of nuclear lamin organization blocks the elongation phase of DNA replication. J Cell Biol. 2000, 149: 1179-1192. 10.1083/jcb.149.6.1179.
Shumaker DK, Solimando L, Sengupta K, Shimi T, Adam SA, Grunwald A, Strelkov SV, Aebi U, Cardoso MC, Goldman RD: The highly conserved nuclear lamin Ig-fold binds to PCNA: its role in DNA replication. J Cell Biol. 2008, 181: 269-280. 10.1083/jcb.200708155.
Bonne G, Di Barletta MR, Varnous S, Becane HM, Hammouda EH, Merlini L, Muntoni F, Greenberg CR, Gary F, Urtizberea JA, Duboc D, Fardeau M, Toniolo D, Schwartz K: Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1999, 21: 285-288. 10.1038/6799.
Hegele RA, Cao H, Liu DM, Costain GA, Charlton-Menys V, Rodger NW, Durrington PN: Sequencing of the reannotated LMNB2 gene reveals novel mutations in patients with acquired partial lipodystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 2006, 79: 383-389. 10.1086/505885.
Padiath QS, Saigoh K, Schiffmann R, Asahara H, Yamada T, Koeppen A, Hogan K, Ptacek LJ, Fu YH: Lamin B1 duplications cause autosomal dominant leukodystrophy. Nat Genet. 2006, 38: 1114-1123. 10.1038/ng1872.
Rankin J, Ellard S: The laminopathies: a clinical review. Clin Genet. 2006, 70: 261-274. 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00677.x.
Bonne G, Levy N: LMNA mutations in atypical Werner's syndrome. Lancet. 2003, 362: 1585-1586.
Szeverenyi I, Cassidy AJ, Chung CW, Lee BT, Common JE, Ogg SC, Chen H, Sim SY, Goh WL, Ng KW, Simpson JA, Chee LL, Eng GH, Li B, Lunny DP, Chuon D, Venkatesh A, Khoo KH, McLean WH, Lim YP, Lane EB: The Human Intermediate Filament Database: comprehensive information on a gene family involved in many human diseases. Hum Mutat. 2008, 29: 351-360. 10.1002/humu.20652.
Stewart CL, Kozlov S, Fong LG, Young SG: Mouse models of the laminopathies. Exp Cell Res. 2007, 313: 2144-2156. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.026.
Mejat A, Misteli T: LINC complexes in health and disease. Nucleus. 2010, 1: 40-52.
Worman HJ, Ostlund C, Wang Y: Diseases of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010, 2: a000760-10.1101/cshperspect.a000760.
Granger B, Gueneau L, Drouin-Garraud V, Pedergnana V, Gagnon F, Ben Yaou R, Tezenas du Montcel S, Bonne G: Modifier locus of the skeletal muscle involvement in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 2011, 129: 149-159. 10.1007/s00439-010-0909-1.
Coffinier C, Chang SY, Nobumori C, Tu Y, Farber EA, Toth JI, Fong LG, Young SG: Abnormal development of the cerebral cortex and cerebellum in the setting of lamin B2 deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010, 107: 5076-5081. 10.1073/pnas.0908790107.
Burke B, Stewart CL: Life at the edge: the nuclear envelope and human disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002, 3: 575-585. 10.1038/nrm879.
Kaufmann SH, Mabry M, Jasti R, Shaper JH: Differential expression of nuclear envelope lamins A and C in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991, 51: 581-586.
Broers JL, Raymond Y, Rot MK, Kuijpers H, Wagenaar SS, Ramaekers FC: Nuclear A-type lamins are differentially expressed in human lung cancer subtypes. Am J Pathol. 1993, 143: 211-220.
Moss SF, Krivosheyev V, de Souza A, Chin K, Gaetz HP, Chaudhary N, Worman HJ, Holt PR: Decreased and aberrant nuclear lamin expression in gastrointestinal tract neoplasms. Gut. 1999, 45: 723-729. 10.1136/gut.45.5.723.
Tilli CM, Ramaekers FC, Broers JL, Hutchison CJ, Neumann HA: Lamin expression in normal human skin, actinic keratosis, squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2003, 148: 102-109. 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2003.05026.x.
Nindl I, Dang C, Forschner T, Kuban RJ, Meyer T, Sterry W, Stockfleth E: Identification of differentially expressed genes in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by microarray expression profiling. Mol Cancer. 2006, 5: 30-10.1186/1476-4598-5-30.
Skvortsov S, Schafer G, Stasyk T, Fuchsberger C, Bonn GK, Bartsch G, Klocker H, Huber LA: Proteomics profiling of microdissected low- and high-grade prostate tumors identifies lamin a as a discriminatory biomarker. J Proteome Res. 2011, 10: 259-268. 10.1021/pr100921j.
Willis ND, Cox TR, Rahman-Casans SF, Smits K, Przyborski SA, van den Brandt P, van Engeland M, Weijenberg M, Wilson RG, de Bruine A, Hutchison CJ: Lamin A/C is a risk biomarker in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2008, 3: e2988-10.1371/journal.pone.0002988.
Sun S, Xu MZ, Poon RT, Day PJ, Luk JM: Circulating Lamin B1 (LMNB1) biomarker detects early stages of liver cancer in patients. J Proteome Res. 2010, 9: 70-78. 10.1021/pr9002118.
Marshall KW, Mohr S, Khettabi FE, Nossova N, Chao S, Bao W, Ma J, Li XJ, Liew CC: A blood-based biomarker panel for stratifying current risk for colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010, 126: 1177-1186.
Wiesel N, Mattout A, Melcer S, Melamed-Book N, Herrmann H, Medalia O, Aebi U, Gruenbaum Y: Laminopathic mutations interfere with the assembly, localization, and dynamics of nuclear lamins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105: 180-185. 10.1073/pnas.0708974105.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S: MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007, 24: 1596-1599. 10.1093/molbev/msm092.
Saitou N, Nei M: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987, 4: 406-425.
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S: Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004, 101: 11030-11035. 10.1073/pnas.0404206101.
Bossie CA, Sanders MM: A cDNA from Drosophila melanogaster encodes a lamin C-like intermediate filament protein. J Cell Sci. 1993, 104: 1263-1272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dittmer, T.A., Misteli, T. The lamin protein family. Genome Biol 12, 222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-222
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-222