Fig. 1
From: The Cpf1 CRISPR-Cas protein expands genome-editing tools
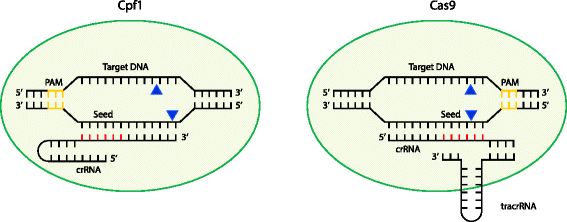
Schematic comparison of target recognition and degradation by Cpf1 and Cas9. An R-loop is formed as a result of protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) recognition (yellow), and subsequent base-pairing interactions occur between the CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and its cognate target sequence. Note that the guide RNA in Cas9 is an RNA duplex involving crRNA and trans-activating CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA), whereas Cpf1 uses a single crRNA. Upon sufficient complementarity in the seed region (red), Cpf1 and Cas9 nucleases will make two single-stranded cuts (blue triangles) resulting in a double-stranded break. DNA and crRNA lengths and cleavage positions are schematic only and are not drawn to scale
