Fig. 1
From: NextDenovo: an efficient error correction and accurate assembly tool for noisy long reads
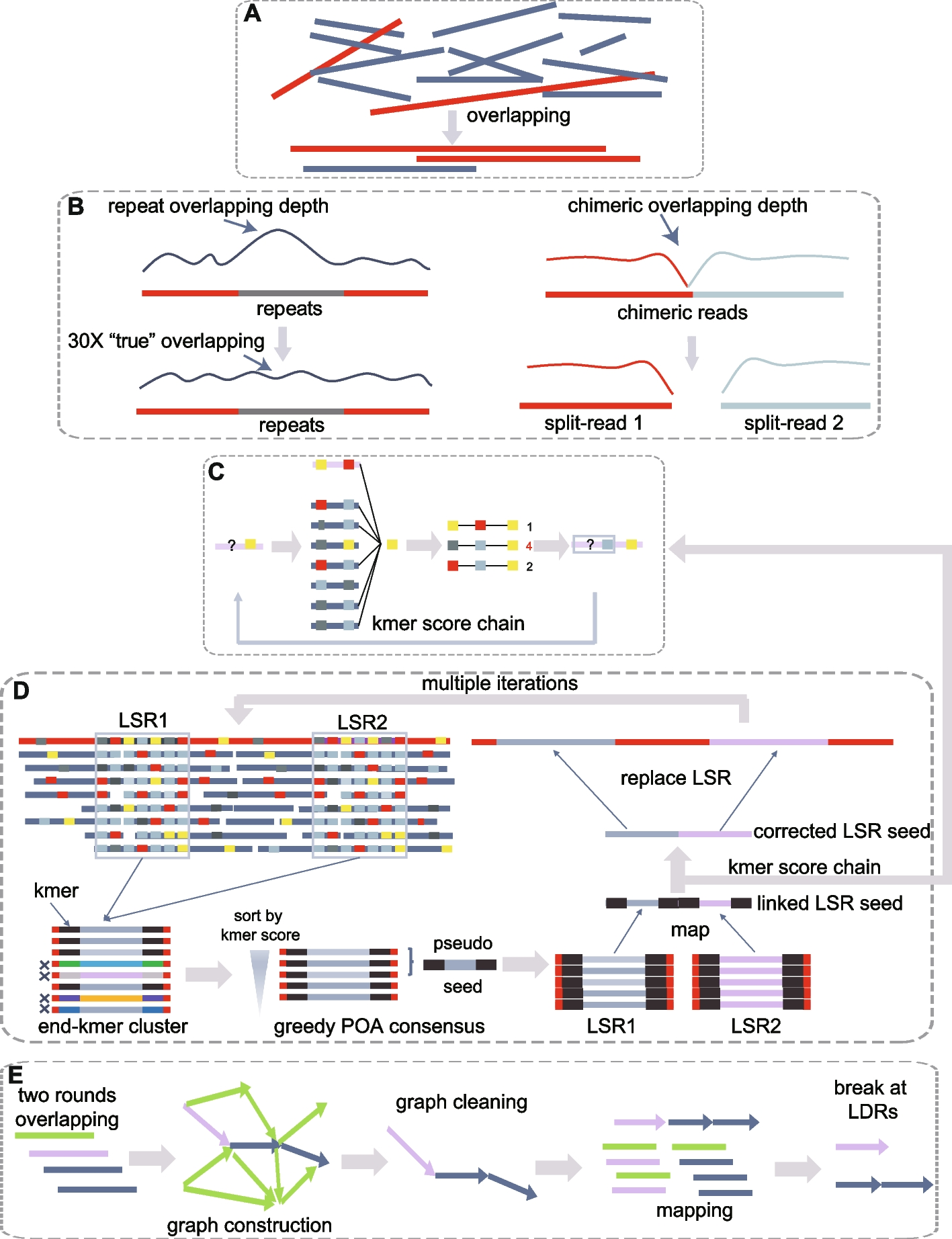
NextDenovo pipeline. A Overlapping reads. B Alignments erroneously caused by repeats were filtered out and chimeric reads were split. C A confidence score was calculated for a given allele at each position with a fixed 3-mer, and the allele with the maximum score was selected as the correct base. The colored rectangles represent the different bases. D NextDenovo first identifies all LSRs at the raw reads, extracts each subsequence spanning these LSRs, and assigns a kmer score to each subsequence. Subsequently, NextDenovo filters out the subsequences with lower scores and produces a pseudo-LSR seed using a greedy POA consensus algorithm, all pseudo-LSR seeds from the same seed being linked as the reference, and all subsequences being mapped to this reference while the KSC algorithm is reapplied to produce a corrected pseudo seed. Then, the corrected LSRs are inserted into the corresponding positions in the raw reads to generate the final corrected reads. E NextDenovo calculates dovetail alignments by two rounds of overlapping, constructs an assembly graph, removes transitive edges, tips, bubbles, and edges with low scores, and generates contigs. Finally, NextDenovo maps all seeds to contigs and breaks a contig if it possesses low-quality regions
